Explore the interplay of geographical features, cultural practices, economic systems, and technological advancements in shaping societies and their development.Throughout history, civilizations have emerged and evolved, shaped by their environments and the needs of their people. While ancient and modern societies may seem worlds apart, they share intriguing similarities that reveal the enduring nature of human experience. From geographic features that dictate settlement patterns to cultural practices that unite communities, the threads of commonality weave a rich tapestry of civilization. Additionally, economic systems and technological advancements, both then and now, reflect our quest for progress and sustainability. In this blog post, we will explore these parallels, shedding light on how the past informs the present and how the core aspects of civilization remain consistent across time. Join us as we delve into the fascinating connections between ancient and modern societies, uncovering the timeless elements that continue to shape our world.
Geographical Features
Both ancient and modern civilizations are significantly influenced by their geographical features. The location of a civilization can dictate its access to resources, climate, and the overall landscape which in turn affects settlement patterns, agricultural practices, and trade routes.
For example, ancient civilizations like the Egyptians thrived along the banks of the Nile River, which provided fertile land due to seasonal flooding. In contrast, modern cities often develop near riverbanks or coastlines, leveraging similar geographical advantages for transportation and trade.
Interestingly, mountainous regions would often lead ancient civilizations, such as the Incas, to develop unique architectural techniques and terrace farming, while contemporary communities in similar regions might embrace tourism and conservation efforts to enhance their economies.
| Feature | Ancient Civilizations | Modern Civilizations |
|---|---|---|
| Access to Water | Nile River | Urban rivers |
| Agricultural Practices | Terrace farming | Modern irrigation |
| Trade Routes | Silk Road | Global shipping lanes |
Cultural Practices
Cultural practices have been the cornerstone of both ancient and modern civilizations, shaping identities and influencing social cohesion. Across the ages, rituals, traditions, and belief systems have provided a sense of belonging and purpose. It’s fascinating to observe how certain core aspects of culture continue to persist, transforming yet retaining their essence over thousands of years.
One of the key similarities is the role of family structures in nurturing cultural values. In ancient societies, families often gathered to celebrate major life events, such as births, marriages, and festivals, fostering community spirit. Modern civilizations follow suit with similar practices, albeit with the influence of contemporary changes. Consider the common practice of holiday celebrations, where families come together to honor their customs, just as their ancestors did.
Furthermore, the transmission of cultural knowledge from one generation to the next has remained remarkably consistent over time. In ancient civilizations, storytelling and oral traditions were prevalent, serving as mediums for passing down knowledge and time-honored practices. Today, technology has transformed these methods, yet the underlying principle of education—whether through books, films, or online platforms—remains the same. This continuity highlights the inherent value placed on cultural heritage across both ancient and modern contexts.
Economic Systems
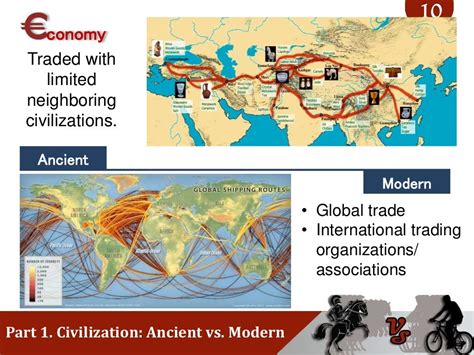
When examining the economic systems of both ancient and modern civilizations, we can observe striking similarities that reveal enduring principles of trade, resource management, and social organization. Ancient economies relied heavily on agriculture, barter systems, and trade routes, much like many aspects of today’s global economy.
For instance, both ancient and modern civilizations have utilized systems of exchange, whether it was through the barter of goods or the use of currency. In ancient times, traders would exchange goods such as spices, textiles, and precious metals. Today, the evolution of the economy has led to sophisticated systems involving digital currencies, stock markets, and global trade agreements.
Moreover, the role of government and regulation in economic systems can be seen across the ages. Ancient societies often employed systems of taxation and regulation to manage resources and ensure social stability. Similarly, modern economies rely on taxation to fund public services and regulate markets to prevent monopolies and ensure fair competition.
| Aspect | Ancient Civilizations | Modern Civilizations |
|---|---|---|
| Trade | Barter and Trade Routes | Currency and Digital Trade |
| Resource Management | Agriculture and Land Use | Global Supply Chains |
| Government Role | Taxation and Regulation | Fiscal Policy and Market Regulation |
In summary, the foundations of economic systems in ancient civilizations set the stage for the complexities of modern economic practices. While technology has transformed these systems fundamentally, the core principles of trade and resource management remain unchanged through time.
Technological Advancements
Throughout history, technological advancements have played a pivotal role in shaping both ancient and modern civilizations. These innovations not only fostered improvements in everyday life but also influenced societal structures and economic systems.
In ancient civilizations, the invention of the wheel, agriculture, and metallurgy greatly enhanced productivity and efficiency. For instance, the ability to cultivate land effectively led to increased food production, consequently allowing societies to thrive and grow. Similarly, the development of tools and machinery paved the way for more complex societal roles and trade systems.
In contrast, modern civilizations have seen rapid technological revolutions that redefine how we connect, communicate, and conduct business. The rise of the internet, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology has transformed industries and everyday life. These advancements have also created a global economy, linking people and markets in ways that were unimaginable in ancient times.
Technological advancements are the backbone of societal evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common traits shared by ancient and modern civilizations?
Both ancient and modern civilizations exhibit structured social hierarchies, established legal systems, and organized economies, reflecting their need for order and progress.
How did religion influence both ancient and contemporary civilizations?
Religion played a crucial role in shaping cultural values, laws, and social norms in both ancient and modern civilizations, often serving as a unifying force among people.
What role does technology play in the development of civilizations?
Technology serves as a catalyst for growth and advancement in both ancient and modern civilizations, facilitating communication, trade, and daily life improvements.
In what ways do ancient civilizations inform our understanding of modern governance?
Ancient civilizations provide insights into governance structures, civic responsibility, and political systems, many of which serve as foundational models for modern governments.
Can cultural practices from ancient civilizations still be seen in modern societies?
Yes, many cultural practices, traditions, and art forms from ancient civilizations have persisted and evolved, influencing modern social customs and artistic expressions.
How did trade impact the relationships between ancient and modern civilizations?
Trade has historically facilitated not only the exchange of goods but also the sharing of ideas, technologies, and cultures, fostering interconnections between civilizations past and present.
What lessons can contemporary societies learn from ancient civilizations?
Contemporary societies can learn valuable lessons on sustainability, conflict resolution, and community building from the successes and failures of ancient civilizations.