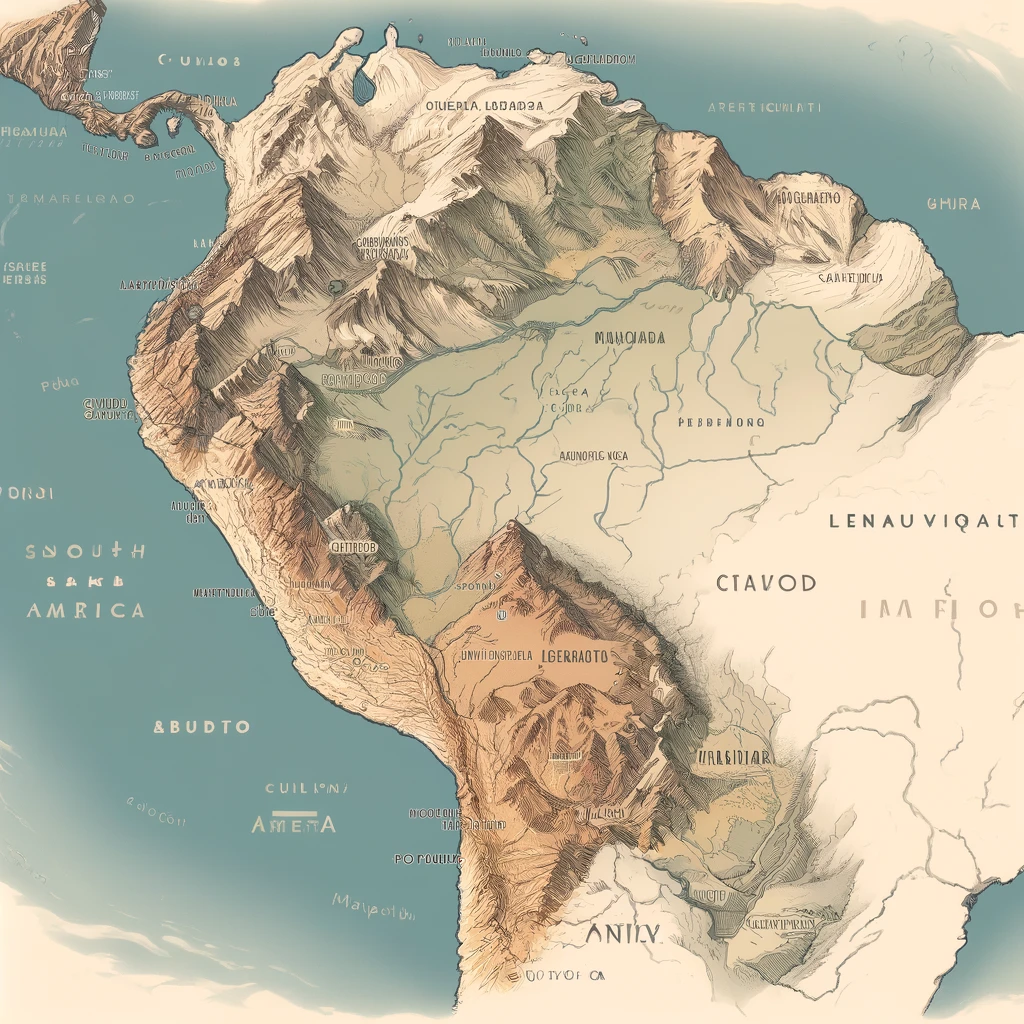
Explore the Inca civilization’s geographic scope, major settlements, and territories in this concise overview of their rich history and culture.The Incas, one of the most remarkable civilizations in history, thrived in the heart of South America long before the advent of modern maps. Known for their incredible architectural achievements and advanced agricultural techniques, the Incas had a profound influence that extended far beyond their immediate surroundings. But where exactly were they located? This blog post will take you on a journey through the geographical landscape of the Inca Empire, exploring its vast expanse from the high peaks of the Andes Mountains to the coastal deserts of Peru. We will look at the major settlements and territories that defined this extraordinary civilization, providing a clearer picture of where the Incas made their mark on the world. Join us as we uncover the impressive geographic scope of the Inca civilization and the legacy it left behind.
Incas: A Brief Overview
The Incas were a prominent civilization that thrived in South America, primarily in the Andes Mountains, between the 15th and 16th centuries. They are best known for their expansive empire, sophisticated agricultural practices, and advanced engineering skills.
The heart of the Inca Empire was located in present-day Peru, with its capital city, Cusco, serving as the political, religious, and cultural center. The Incas developed a road system that stretched across their territory, allowing for efficient communication and trade. At its height, the empire included parts of modern-day Ecuador, Bolivia, Argentina, Chile, and Colombia.
Incas left a lasting legacy, particularly in architecture and agriculture, with famous sites like Machu Picchu showcasing their ingenuity. The civilization effectively managed vast areas through a centralized government, which implemented a system of mit’a (labor tax) that required citizens to contribute labor for public works projects.
Inca Civilization’s Geographic Scope
The Inca Civilization was one of the most remarkable and expansive empires in history, encompassing a vast geographic area across the western coast of South America. At its peak, the Inca Empire stretched over 2,500 miles along the Andes Mountains, and its territory included what is now Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, Chile, and parts of Argentina and Colombia.
To understand the scope of the Inca Civilization, it’s essential to break down the key regions that were influenced by this incredible culture. The core of the empire was located in the highlands of Peru, where the administrative, religious, and cultural center, Cusco, flourished. This ancient city was not only a spiritual heart but also a significant hub for trade and governance.
Moreover, the Inca constructed an extensive network of roads and bridges that connected various regions, allowing for efficient movement of their armies and resources. These roads facilitated trade and cultural exchange across diverse terrains, from the coastal deserts to the steep mountain passes, showcasing the Incas’ engineering prowess.
| Region | Modern Countries |
|---|---|
| Andean Highlands | Peru, Bolivia |
| Coastal Areas | Peru, Chile |
| Lower River Valleys | Ecuador, Argentina |
| Forested Regions | Colombia |
This table illustrates some key geographic areas of the Inca Empire and the modern countries that encompass them. Such data reveals the enormous extent of the Inca Civilization’s influence, both culturally and economically.
Ultimately, the geographical scope of the Inca Civilization illustrates its incredible adaptability and extensive control over a diverse range of landscapes and peoples, further solidifying its status as one of history’s most significant civilizations.
Incas’ Major Settlements and Territories
The Inca Empire was one of the largest empires in pre-Columbian America, stretching across modern-day Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, and parts of Chile and Argentina. Its vast geography contributed to the diversity of its cultures and societies.
| Settlement | Region | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Cusco | Peru | Capital city and center of the empire, known for its architectural marvels. |
| Machu Picchu | Peru | A prominent Inca citadel set high in the Andes, showcasing remarkable urban planning. |
| Arequipa | Peru | Strategic location for trade and agriculture, known for its volcanic rock architecture. |
| Quito | Ecuador | Key administrative and trade center connecting northern territories. |
| La Paz | Bolivia | Crucial area for control and expansion of Incan influence across the region. |
These settlements were not only centers of governance and trade but also hubs for cultural exchange and innovation. The Incas developed extensive road networks, which facilitated the movement of people, goods, and ideas throughout their empire. Their ability to manage such vast territories is a testament to their organizational skills and architectural genius.
Furthermore, the Incas established agricultural terracing in their settlements, which allowed them to cultivate crops at varying altitudes. This innovation significantly contributed to their food security and agricultural diversity, showcasing their advanced techniques in farming.
In summary, the Incas left an indelible mark on the regions they inhabited. Their major settlements and territories were carefully planned and executed, ens
Frequently Asked Questions
The Incas primarily inhabited areas of modern-day Peru, but their empire also extended into parts of Ecuador, Bolivia, Colombia, and Chile.The capital city of the Inca Empire was Cusco, which is located in present-day Peru.The Incas thrived in the Andean mountains, which provided natural barriers for protection, fertile land for agriculture, and access to important resources like minerals.The Inca road system was extensive, connecting various parts of the empire with rugged terrain, included thousands of miles of roads, and allowed for efficient communication and transport.Machu Picchu is one of the most famous archaeological sites associated with the Incas, often referred to as the 'Lost City of the Incas'.The Andes Mountains were crucial to Inca culture, serving as both a barrier to invaders and a source of resources, as well as influencing their agricultural practices and religious beliefs.The Inca Empire expanded through a combination of military conquest, strategic alliances, and the incorporation of local tribes through a diplomatic approach to governance.